
A study in which CEF members collaborated assessed the influence of the chemical variables of poplar biomass on its suitability for torrefaction, highlighting the relevance of the analytical pyrolysis technique for classifying and optimizing the process.
The article was developed in collaboration by three members of the Forest Research Centre (CEF) – Researchers José Carlos Rodrigues and Ana Alves, and Professor José Graça – and one member of the Instituto Nacional de Investigação Agrária (INIAV) – Researcher Abel Rodrigues – to assess the influence of chemical composition (determined by analytical pyrolysis) on the torrefaction of poplar biomass.
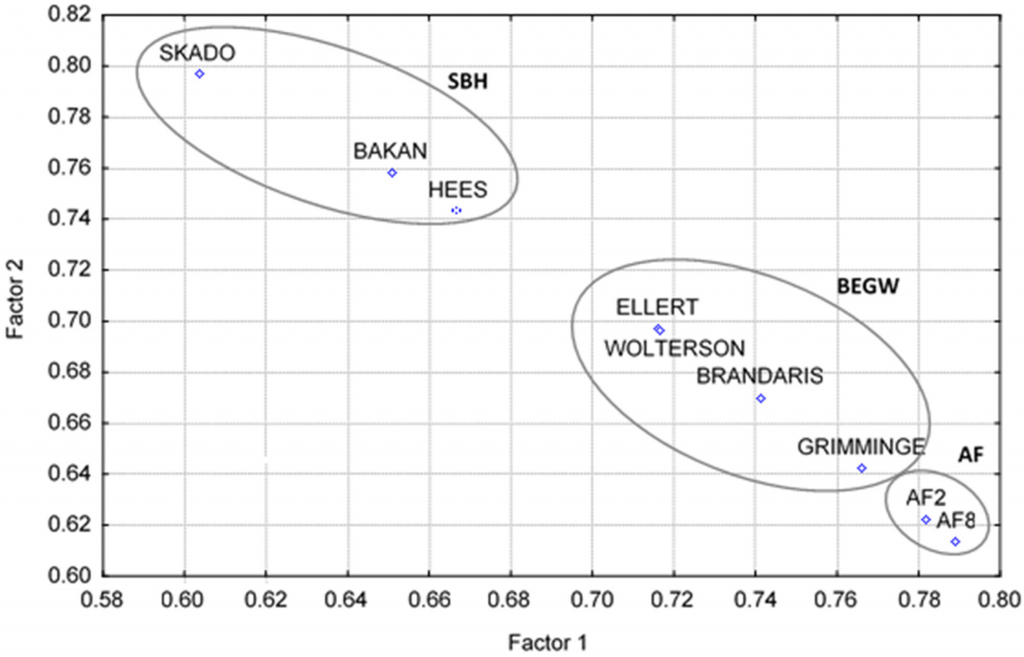
This study aimed to evaluate the influence in torrefaction of the chemical structure of biomasses from nine poplar commercial SRC clones, evaluated through analytical pyrolysis. Factorial and discriminant analysis allowed for clustering the tested clones in three groups, evidencing relevant influences of (S/G) ratio, Py-lignin, and, to a lesser extent, (cP/cH) ratio in the classification of these groups, clearly showing the impact of chemical variables of feedstock in torrefaction. The results contribute: (i) to the validation of use of the expedite analytical pyrolysis technique for classification of biomasses in accordance with their torrefaction aptitude and, thereby, (ii) to optimizing strategies in technological issues as diverse as poplar clone genetic breeding and modeling biomass torrefaction and pyrolysis.
Published in the journal Molecules by MDPI, the article “A Quantitative Evaluation of the Influence of Chemical Variables of Biomasses of Poplar SRC Commercial Clones in Torrefaction” is available for consultation at https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/29/19/4542.














